Thursday, 4 July 2013
Links on Avoiding Pain
 This week, as I have before in this blog, I am posting a set of new links to other web sites that discuss a subject covered in The Brain from Top to Bottom. The subject this week is the sub-topic “Avoiding Pain”, under the topic “Pleasure and Pain”. For each link, I also provide a brief description of the content on the site in question. (more…)
This week, as I have before in this blog, I am posting a set of new links to other web sites that discuss a subject covered in The Brain from Top to Bottom. The subject this week is the sub-topic “Avoiding Pain”, under the topic “Pleasure and Pain”. For each link, I also provide a brief description of the content on the site in question. (more…)
Pleasure and Pain | Comments Closed
Monday, 24 June 2013
The Complementarity of the Brain’s Two Hemispheres
 Einstein said that intuition is a gift, and rationality is its servant. But in another RSA Animate lecture to which we provide a link this week, about the specialization of the two hemispheres of the human brain, psychiatrist and author Iain McGilchrist says that we have created a society that honours the servant but has forgotten the gift. (more…)
Einstein said that intuition is a gift, and rationality is its servant. But in another RSA Animate lecture to which we provide a link this week, about the specialization of the two hemispheres of the human brain, psychiatrist and author Iain McGilchrist says that we have created a society that honours the servant but has forgotten the gift. (more…)
From Thought to Language | Comments Closed
Tuesday, 18 June 2013
Proteins That Guide the Wiring of the Brain
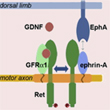
The human brain has millions of times more connections between its neurons than the number of genes (roughly 20 000 to 25 000) in the DNA of these cells. And yet, when the brain is developing, the tips of the axons of its growing neurons act like veritable homing devices, successfully seeking out their specific targets in the complex molecular soup that constitutes the extracellular environment.
Scientists have long known that these targets produce molecules that are detected by receptors on the axons’ growth cones and guide them to their targets. But only recently did a team at the Salk Institute in California discover how just a handful of genes enable the guidance processes by which the brain’s complex wiring is established. (more…)
How the Mind Develops | Comments Closed
Tuesday, 11 June 2013
Shedding Some Light on the First Cell Membranes
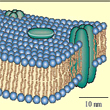 Every living cell, including every neuron, has a cell membrane that separates the outside environment from the myriad biochemical reactions that take place inside the cell. Some of these enzymatic reactions are even involved in forming this membrane. It is this characteristic of living things—their ability to produce themselves—that Maturana and Varela have called autopoiesis.
Every living cell, including every neuron, has a cell membrane that separates the outside environment from the myriad biochemical reactions that take place inside the cell. Some of these enzymatic reactions are even involved in forming this membrane. It is this characteristic of living things—their ability to produce themselves—that Maturana and Varela have called autopoiesis.
But if it takes a membrane for there to be a living cell, and if it is the living cell that produces the membrane, then how do we solve this dilemma, which is similar in every way to the classic question, “Which came first, the chicken or the egg?” The only logical assumption is that at some moment at the start of evolution, a biochemical reaction capable of creating membranes was catalyzed by a non-organic molecule (a molecule that did not result from the metabolism of a living cell).
That is exactly the kind of reaction that chemists Neal Devaraj and Itay Budin have just managed to achieve. (more…)
From the Simple to the Complex | Comments Closed
Monday, 3 June 2013
Seeing What’s in Your Eye
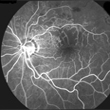
The structure of your eye is a lot like that of a traditional film camera. The lens of your eye is like the camera’s lens. Your iris is like the diaphragm, and your retina, at the very back of the eye, acts like the light-sensitive film.
However, there is a hole in your retina that lets the axons of its ganglion cells (a kind of neuron) exit the eye while letting blood vessels enter to irrigate all of the retina’s neurons. This hole creates a true “blind spot” in your field of vision. You don’t notice this blind spot in your daily life. (more…)
The Senses | Comments Closed








